This example shows how to read and write data to and from an SD card. Please click here for more information on the SD library.
The Arduino board has to be connected to the Ethernet Shield and also has a USB cable connected to the computer.
http://news.chivindo.com/681/using-the-sd-library-to-read-and-write-to-a-file-on-a-sd-card.html
Step 1: What You Need?
1 x Arduino Board ( Arduino UNO used in this tutorial)
1 x Arduino Ethernet Shield (or other board with an SD slot)
1 x Formatted SD card
1 x Arduino Ethernet Shield (or other board with an SD slot)
1 x Formatted SD card
1 x USB Type-B Cable
Don't have components? Don't worry. Just click the component's name.
Step 2: Build Your Circuit.
Step 3: Upload The Code.
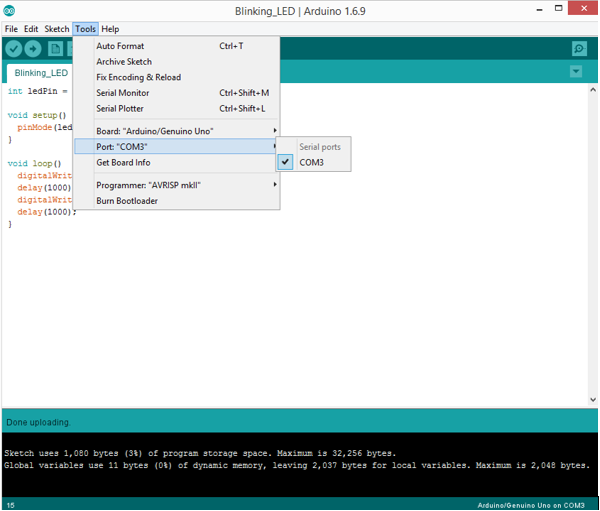
1. Select the Arduino board type: Select Tools >> Board >> Select your correct Arduino board used.2. Find the port number by accessing device manager on Windows. See the section Port (COM&LPT) and look for an open port named "Arduino Uno (COMxx)". If you are using a different board, you will find a name accordingly. What matters is the xx in COMxx part. In my case, it's COM3. So my port number is 3.
Select the right port: Tools >> Port >> Select the port number.

3. You can find this code in the example of Arduino IDE.
Select File >> Examples >> SD >> ReadWrite
Click press the "upload" button (see the button with right arrow mark).
/*
SD card read/write This example shows how to read and write data to and from an SD card file
The circuit:
* SD card attached to SPI bus as follows:
** MOSI - pin 11
** MISO - pin 12
** CLK - pin 13
** CS - pin 4 created Nov 2010
by David A. Mellis
modified 9 Apr 2012
by Tom Igoe This example code is in the public domain. */ #include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h> File myFile; void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
} Serial.print("Initializing SD card..."); if (!SD.begin(4)) {
Serial.println("initialization failed!");
return;
}
Serial.println("initialization done."); // open the file. note that only one file can be open at a time,
// so you have to close this one before opening another.
myFile = SD.open("test.txt", FILE_WRITE); // if the file opened okay, write to it:
if (myFile) {
Serial.print("Writing to test.txt...");
myFile.println("testing 1, 2, 3.");
// close the file:
myFile.close();
Serial.println("done.");
} else {
// if the file didn't open, print an error:
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
} // re-open the file for reading:
myFile = SD.open("test.txt");
if (myFile) {
Serial.println("test.txt:"); // read from the file until there's nothing else in it:
while (myFile.available()) {
Serial.write(myFile.read());
}
// close the file:
myFile.close();
} else {
// if the file didn't open, print an error:
Serial.println("error opening test.txt");
}
} void loop() {
// nothing happens after setup
}
The code below is configured for use with an Ethernet shield, which has an onboard SD slot. In the setup(), we call SD.begin(), naming pin 4 as the CS pin. This pin varies depending on the make of shield or board you are using.
In setup(), create a new file with SD.open() named "test.txt". FILE_WRITE enables read and write access to the file, starting at the end. If a file "test.txt" was already on the card, that file would be opened.
Name the instance of the opened file "myFile".
Once opened, use myFile.println() to write a string to the card, followed by a carriage return. Once the content is written, close the file.
Again, open the file with SD.open(). Once opened, ask the Arduino to read the contents of the file with SD.read() and send them over the serial port. After all the contents of the file are read, close the file with SD.close().


Comments
Post a Comment