One of the major development directions in the energy sector is the widespread usage of renewable energy technologies. The keen interest in alternative energy resources is mainly due to the fact that they are environmentally-friendly and thus make it possible to reduce the negative environmental impact of the energy industry, increasing the levels of energy and ecological safety.
The modern energy industry is mainly dependent on non-renewable energy resources, which are limited and cannot guarantee the sustainable development of the world’s energy sector in the long term period. Another substantial drawback of using non-renewables is their devastating effect on the environment.
In contrast, the non-conventional or alternative energy relies on solar power, wind power, geothermal energy, biomass, hydro power, which are potentially infinite in the foreseeable future. All renewables can be divided into two groups: those using direct solar power and those reliant on its secondary manifestations (indirect solar power) as well as the energy of interaction between the Sun, Moon, and Earth.
The indirect activity of the Sun results in respective effects in the atmosphere, hydrosphere and geosphere, mainly in wind power, hydro power, the energy of waves, tidal energy, geothermal energy, etc. Also, the non-conventional renewable energy includes small hydropower with hydro power plants, the capacity of which is up to 30 MW, or even up to 10 MW in some countries.
Compared to conventional unsustainable sources, the main benefits of renewables are that they are next to infinite and diminish the negative effects on the environment, such as the greenhouse effect, radioactive and thermal pollution, etc.
Rising Energy Demands to Shape the Future Energy Systems
The main factors limiting the usage of non-conventional renewables are the following:
At the same time, the need to use alternative sources is defined by the fast growth of energy demand, which, compared to the year 2000, is expected to increase by two by the year 2030, and by 4 by the year 2050; the prospective depletion of the known natural fuel resources; the critical condition of the environment due to it being polluted with nitrogen and sulfur oxides, carbon dioxide, dust-like particles caused by fuel combustion, radioactive and thermal pollution, etc.
Renewable energy resources have some conceptual differences, so the ability to use them efficiently is based on the scientifically developed principles of converting renewable energy into the type of energy required by consumers. The environment always has the flows of renewable energy, so in the process of alternative energy development it is crucial to take advantage of local energy resources, while selecting those most efficient.
The use of renewable resources should be multivariable and complex, which will facilitate a particular region’s economic development. For instance, alternative energy resources can be found in agro-industrial systems, where animal and garden waste is used for obtaining biogas, liquid and solid fuel, and for producing fertilizers.
The effective planning of renewable-based energy systems involves the following:
One of the main characteristics of renewable energy sources is their energy potential. This parameter represents the amount of energy typical of the respective renewable resource. For evaluation purposes the renewable energy sources are differentiated as having the following energy potential:
The approximate data on the world’s renewable energy sources are shown in the table below.
 http://news.chivindo.com/372/non-conventional-sources-of-energy-general-information.html
http://news.chivindo.com/372/non-conventional-sources-of-energy-general-information.html
Renewable versus Non-Renewable Energy Sources
The conventional sources of energy are represented by non-renewable resources such as coal, natural gas, oil and uranium; while renewable sources include hydropower and fuel wood.The modern energy industry is mainly dependent on non-renewable energy resources, which are limited and cannot guarantee the sustainable development of the world’s energy sector in the long term period. Another substantial drawback of using non-renewables is their devastating effect on the environment.
In contrast, the non-conventional or alternative energy relies on solar power, wind power, geothermal energy, biomass, hydro power, which are potentially infinite in the foreseeable future. All renewables can be divided into two groups: those using direct solar power and those reliant on its secondary manifestations (indirect solar power) as well as the energy of interaction between the Sun, Moon, and Earth.
The indirect activity of the Sun results in respective effects in the atmosphere, hydrosphere and geosphere, mainly in wind power, hydro power, the energy of waves, tidal energy, geothermal energy, etc. Also, the non-conventional renewable energy includes small hydropower with hydro power plants, the capacity of which is up to 30 MW, or even up to 10 MW in some countries.
Compared to conventional unsustainable sources, the main benefits of renewables are that they are next to infinite and diminish the negative effects on the environment, such as the greenhouse effect, radioactive and thermal pollution, etc.
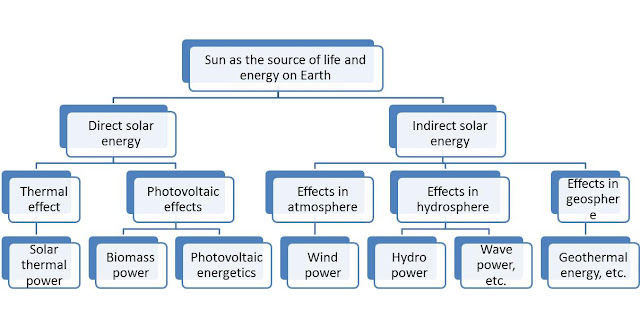 |
Types of Renewable Energy |
The main factors limiting the usage of non-conventional renewables are the following:
- the low density of the power flow, which, for instance, is 1.36·10-3 MW/m2 for solar energy on the Earth surface, wind power at a wind speed of 10 m/s – 6·10-4 MW/m2, geothermal – 3·10-8 mW/m2, whereas for the nuclear power it is 0.2 MW/m2;
- the uneven generation and consumption of energy;
- the relatively high cost of generating units and of energy generation.
At the same time, the need to use alternative sources is defined by the fast growth of energy demand, which, compared to the year 2000, is expected to increase by two by the year 2030, and by 4 by the year 2050; the prospective depletion of the known natural fuel resources; the critical condition of the environment due to it being polluted with nitrogen and sulfur oxides, carbon dioxide, dust-like particles caused by fuel combustion, radioactive and thermal pollution, etc.
Renewable energy resources have some conceptual differences, so the ability to use them efficiently is based on the scientifically developed principles of converting renewable energy into the type of energy required by consumers. The environment always has the flows of renewable energy, so in the process of alternative energy development it is crucial to take advantage of local energy resources, while selecting those most efficient.
The use of renewable resources should be multivariable and complex, which will facilitate a particular region’s economic development. For instance, alternative energy resources can be found in agro-industrial systems, where animal and garden waste is used for obtaining biogas, liquid and solid fuel, and for producing fertilizers.
The effective planning of renewable-based energy systems involves the following:
- regular research of the environment similar to geological exploration done when searching for oil or gas;
- studying the region’s energy demands in industrial manufacturing, agricultural production and household requirements. To put it in other words, to select the most economical source of energy, it is important to know the structure of energy consumers.
Potential of Renewable Energy
One of the main characteristics of renewable energy sources is their energy potential. This parameter represents the amount of energy typical of the respective renewable resource. For evaluation purposes the renewable energy sources are differentiated as having the following energy potential:
- theoretical, defined as the total amount of energy;
- technical, defined as part of the theoretical potential, which can be utilized with the contemporary equipment;
- economic, defined as the part of energy potential, which is reasonable to use considering economic, social, ecologic and other factors.
The approximate data on the world’s renewable energy sources are shown in the table below.
Energy potential of renewable energy sources
Renewable energy resources | Potential, billion tons of oil equivalent / year | |
Technical | Economic | |
Direct solar power | 5 | 1 |
Thermal energy of seas and oceans | 1 | 0.1 |
Wind power | 5 | 1 |
Hydro power, including: | ||
- energy of currents | 4.5 | 2.6 |
- energy of waves | 0.05 | 0.01 |
- tidal energy | 0.7 | – |
Biomass power (excluding wood fuel) | 2.55 | 2.0 |
Geothermal energy | 0.4 | 0.2 |
Source (Russian language): http://energetika.in.ua
About KEP
KEP (KharkovEnergoPribor Ltd.) produces high voltage testing equipment, including portable testing instruments and cable test vans, for the world’s leading power engineering companies. The KEP’s product range includes solutions for cable tracing, cable diagnostics and fault locating, testing high voltage instruments and safety gear, and oil dielectric testing.
We at KEP believe that our main task is to translate the customer’s requirements into the top-quality product, combining cutting-edge technology with fundamental high voltage testing principles.
Alexei Tiatiushkin
Marketing manager
KharkovEnergoPribor Ltd.
marketing@keppowertesting.uk

Comments
Post a Comment